Writing Clear and Measurable Learning Objectives
Learning objectives aren’t just a list of what you’re covering in class. Good learning objectives are what you want your students/trainees to learn or achieve. When you begin creating a course, you want to design with the end in mind.
Effective learning objectives use action verbs to describe what you want your students to demonstrate in terms of knowledge, skills, and values upon completion of the course.
1. Identify the Level of Knowledge Necessary to Achieve Your Objective
Before you begin writing objectives, stop and think about what type of change you want your training to make. In other words, what do you want your participants to do differently when they return to work?
Effective learning objectives use action verbs to describe what you want your students to demonstrate in terms of knowledge, skills, and values upon completion of the course.
1. Identify the Level of Knowledge Necessary to Achieve Your Objective
Before you begin writing objectives, stop and think about what type of change you want your training to make. In other words, what do you want your participants to do differently when they return to work?
2. Select an Action Verb
Use an action verb to describe the behavior at the appropriate level of learning. Avoid having more than one action verb for each level of learning, and make sure it’s a verb that can be measured.
3. Check Your Objective
Make sure your objectives include four pieces: audience, behavior, condition, and degree of mastery. For every one, identify and label the component. Here are the A, B, C, D's every objective should contain:
- Audience: It’s important that your objective identifies the people that will be doing the learning. Typically this will involve the word, “learner” or “participant.”
- Behavior: You’ll need to identify what the participants are going to do differently. This component will contain your action verb.
- Condition: This part of the objective will describe the situation of the participants.
- Degree of Mastery: This part of the objective is closely tied to the change in behavior, as it stipulates the degree of the change.
Example 1
Given an expense report, the learner will complete the company form with no errors.
Example 2
After completing the three-day design training, the learner will be able to list the 8 steps in the design process in order.
Additional Learning Objectives Resources
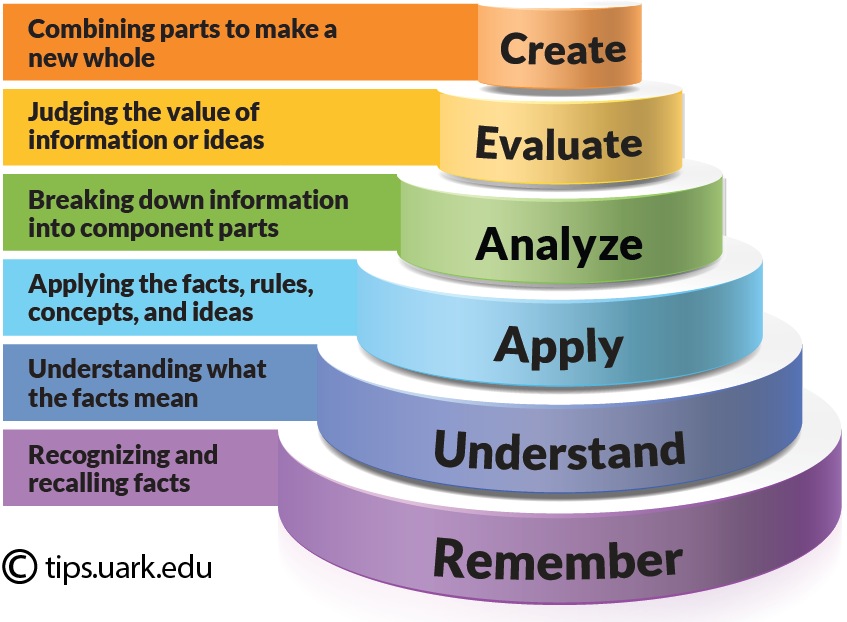
Bloom's Taxonomy - 6 levels of learning
<p>Bloom’s Taxonomy is a classification of the different objectives and skills that educators set for their students (learning objectives). The taxonomy was proposed in 1956 by Benjamin Bloom, an educational psychologist at the University of Chicago. The terminology has been recently updated to include the following six levels of learning. These 6 levels can be used to structure the learning objectives, lessons, and assessments of your course. :</p>
<ol>
<li><strong>Remembering:</strong> Retrieving, recognizing, and recalling relevant knowledge from long‐term memory.</li>
<li><strong>Understanding:</strong> Constructing meaning from oral, written, and graphic messages through interpreting, exemplifying, classifying, summarizing, inferring, comparing, and explaining.</li>
<li><strong>Applying:</strong> Carrying out or using a procedure for executing, or implementing.</li>
<li><strong>Analyzing:</strong> Breaking material into constituent parts, determining how the parts relate to one another and to an overall structure or purpose through differentiating, organizing, and attributing.</li>
<li><strong>Evaluating:</strong> Making judgments based on criteria and standards through checking and critiquing.</li>
<li><strong>Creating:</strong> Putting elements together to form a coherent or functional whole; reorganizing elements into a new pattern or structure through generating, planning, or producing.</li>
</ol>
<p>Like other taxonomies, Bloom’s is hierarchical, meaning that learning at the higher levels is dependent on having attained prerequisite knowledge and skills at lower levels. You will see Bloom’s Taxonomy often displayed as a pyramid graphic to help demonstrate this hierarchy. We have updated this pyramid into a “cake-style” hierarchy to emphasize that each level is built on a foundation of the previous levels.<br />
<br />
<img title="Blooms_Taxonomy_pyramid_cake-style" alt="Blooms" src="/images/librariesprovider16/default-album/blooms_taxonomy_pyramid_cake-style76d428ddb07d6e0c8f46ff0000eea05b.jpg?sfvrsn=39a9468a_0" displaymode="Thumbnail" sfref="[images|librariesProvider16]7dd428dd-b07d-6e0c-8f46-ff0000eea05b" /></p>
List of Mearsurable Verbs
<div>
<h2>List of Measurable Verbs Used to Assess Learning Outcomes</h2>
</div>
<div><em>Bloom's Taxonomy of Educational Objectives (1956): Cognitive Skills</em><br />
A group of educators, led by Benjamin Bloom, identified a hierarchy of six categories of cognitive skills: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis and evaluation. As students learn, they start with the knowledge level and progress through the hierarchy. Thus, advanced courses should include skills at a higher level than introductory or basic skills courses. Below you will find a web-resource as well as a list of measurable verbs to assist you in writing course objectives and assess learning outcomes.<br />
<br />
</div>
<span style="text-decoration: underline;"><strong>Knowledge Level</strong></span>: The successful student will recognize or recall learned information.
<blockquote>
<table style="width: 450px;" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="0">
<tbody>
<tr style="width: 45px;">
<td align="left" valign="middle" style="width: 150px;">
<p>list </p>
</td>
<td>
<p>record</p>
</td>
<td style="width: 150px;">
<p>underline</p>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>state</td>
<td>define</td>
<td>arrange</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>name</td>
<td>relate</td>
<td>describe</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>tell</td>
<td>recall</td>
<td>memorize</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>recall</td>
<td>repeat</td>
<td>recognize</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>label</td>
<td>select</td>
<td>reproduce</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</blockquote><span style="text-decoration: underline;"><strong>Comprehension Level</strong></span>: The successful student will restate or interpret information in their own words.<br />
<blockquote>
<table style="width: 450px;" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="0">
<tbody>
<tr style="width: 45px;">
<td align="left" valign="middle" style="width: 150px;">
<p>explain</p>
</td>
<td>
<p>describe</p>
</td>
<td style="width: 150px;">
<p>report</p>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>translate</td>
<td>express</td>
<td>summarize</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>identify</td>
<td>classify</td>
<td>discuss</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>restate</td>
<td>locate</td>
<td>compare</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>discuss</td>
<td>review</td>
<td>illustrate</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>tell</td>
<td>critique</td>
<td>estimate</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>reference</td>
<td>interpret</td>
<td>reiterate</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</blockquote><span style="text-decoration: underline;"><strong>Application Level</strong></span>: The successful student will use or apply the learned information.<br />
<blockquote>
<table style="width: 450px;" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="0">
<tbody>
<tr style="width: 45px;">
<td align="left" valign="middle" style="width: 150px;">
<p>apply </p>
</td>
<td>
<p>sketch</p>
</td>
<td style="width: 150px;">
<p>perform</p>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>use</td>
<td>solve</td>
<td>respond</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>practice</td>
<td>construct</td>
<td>role-play</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>demonstrate</td>
<td>conduct</td>
<td>execute</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>complete</td>
<td>dramatize</td>
<td>employ</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</blockquote><span style="text-decoration: underline;"><strong>Analysis Level</strong></span>: The successful student will examine the learned information critically.<br />
<blockquote>
<table style="width: 450px;" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="0">
<tbody>
<tr style="width: 45px;">
<td align="left" valign="middle" style="width: 150px;">
<p>analyze </p>
</td>
<td>
<p>inspect</p>
</td>
<td style="width: 150px;">
<p>test</p>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>distinguish</td>
<td>categorize</td>
<td>critique</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>differentiate</td>
<td>catalogue</td>
<td>diagnose</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>appraise</td>
<td>quantify</td>
<td>extrapolate</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>calculate</td>
<td>measure</td>
<td>theorize</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>experiment</td>
<td>relate</td>
<td>debate</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</blockquote><span style="text-decoration: underline;"><strong>Synthesis Level</strong></span>: The successful student will create new models using the learned information.<br />
<blockquote>
<table style="width: 450px;" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="0">
<tbody>
<tr style="width: 45px;">
<td align="left" valign="middle" style="width: 150px;">
<p>develop </p>
</td>
<td>
<p>revise</p>
</td>
<td style="width: 150px;">
<p>compose</p>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>plan</td>
<td>formulate</td>
<td>collect</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>build</td>
<td>propose</td>
<td>construct</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>create</td>
<td>establish</td>
<td>prepare</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>design</td>
<td>integrate</td>
<td>devise</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>organize</td>
<td>modify</td>
<td>manage</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</blockquote><span style="text-decoration: underline;"><strong>Evaluation Level</strong></span>: The successful student will assess or judge the value of learned information.<br />
<blockquote>
<table style="width: 450px;" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="0">
<tbody>
<tr style="width: 45px;">
<td align="left" valign="middle" style="width: 150px;">
<p>review </p>
</td>
<td>
<p>appraise</p>
</td>
<td style="width: 150px;">
<p>choose</p>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>justify</td>
<td>argue</td>
<td>conclude</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>assess</td>
<td>rate</td>
<td>compare</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>defend</td>
<td>score</td>
<td>evaluate</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>report on</td>
<td>select</td>
<td>interpret</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>investigate</td>
<td>measure</td>
<td>support</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</blockquote>
<br />
Bloom's Taxonomy Action Verbs
<a title="BloomsLevel" href="/docs/librariesprovider16/default-document-library/bloomslevel.pdf?sfvrsn=88a0468a_0" target="_blank" sfref="[documents|librariesProvider16]ccdd28dd-b07d-6e0c-8f46-ff0000eea05b">BloomsLevel</a><br />
Bloom's Example Learning Objectives
<table width="668" border="1" cellpadding="15">
<tbody>
<tr>
<th width="107" height="73" scope="col">Bloom’s Level</th>
<th width="221" scope="col">Key Verbs (keywords)</th>
<th width="234" scope="col">Example Learning Objective</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td style="background-color: #f68c1e;"><strong>Create</strong></td>
<td>design, formulate, build, invent, create, compose, generate, derive, modify, develop.</td>
<td><em>By the end of this lesson, the student will be able to design an original homework problem dealing with the principle of conservation of energy.</em></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td style="background-color: #fdc20e;"><strong>Evaluate</strong></td>
<td>choose, support, relate, determine, defend, judge, grade, compare, contrast, argue, justify, support, convince, select, evaluate.</td>
<td>By the end of this lesson, the student will be able to determine whether using conservation of energy or conservation of momentum would be more appropriate for solving a dynamics problem.</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td style="background-color: #89b83f;"><strong>Analyze</strong></td>
<td>classify, break down, categorize, analyze, diagram, illustrate, criticize, simplify, associate.</td>
<td><em>By the end of this lesson, the student will be able to </em>differentiate between potential and kinetic energy.</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td style="background-color: #78d1f0;"><strong>Apply</strong></td>
<td>calculate, predict, apply, solve, illustrate, use, demonstrate, determine, model, perform, present.</td>
<td><em>By the end of this lesson, the student will be able to </em>calculate the kinetic energy of a projectile.</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td style="background-color: #6c94c4;"><strong>Understand</strong></td>
<td>describe, explain, paraphrase, restate, give original examples of, summarize, contrast, interpret, discuss.</td>
<td><em>By the end of this lesson, the student will be able to </em>describe Newton’s three laws of motion to in her/his own words</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td style="background-color: #aa7fb8;"><strong>Remember</strong></td>
<td>list, recite, outline, define, name, match, quote, recall, identify, label, recognize.</td>
<td><em>By the end of this lesson, the student will be able to </em>recite Newton’s three laws of motion.</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<p><em>Learning objective examples adapted from, Nelson Baker at Georgia Tech: nelson.baker@pe.gatech.edu</em></p>

